Influence of substances concentrations on the velocity of chemical reaction
For substances to react the molecules they consist of must collide.
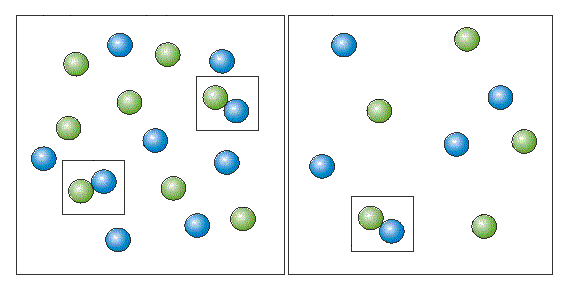
As the collision of two people in a crowded street is more probable, than in a deserted one.
The same with molecules. The probability of molecular collision is obviously higher when there
are more molecules per volume unit (left figure). It's directly proportional to number of molecules
per volume unit, i.e. to the molar concentrations of reagents. It could clearly be shown by the model.
In the middle of the XIX century (1865 - N.N. Beketov, 1867 - C.M. Guldberg, P. Waage)
the basic postulate of chemical kinetics called also the law of mass action was formulated:
|
The velocity of chemical reaction at a given moment of time is proportional
to the concentrations of reagents raised to certain power:
v = k[A]n[B]m, for reaction aA + bB = ...
|
Numbers n, m in terms of the law of mass actions are referred to as orders of reaction
of appropriate substances. These are experimentally determined values. The sum of indexes of
powers n and m is referred to as overall order of reaction.
Please, pay attention, that the powers of concentrations A and B in general are not equal to
stoichiometric coefficients of reaction. They become numerically equal only
in the case when reaction does proceed as it written down (such reactions are referred to
as simple or elementary and are rare enough). IIn most cases the reaction equation demonstrates
only the result of chemical process, but not its mechanism.
Do you want to know, why?
The coefficient k is called the constant of the velocity of reaction.
It is a constant value for the given reaction at the given temperature.
*If the reaction includes a solid substance as a reagent, its concentration
is omitted from the formula for the velocity, the cause of this is that the reactions of solid substances
proceed on their surface, where the concentration of the solid is constant, so it can be combined
with the constant of the velocity of reaction.
Csolid+O2=CO2,
v=k[C]m[O2]n=k'[O2]n; k'=k[C]m
Supplementary
| 



